DIY Body Scrubs (4 Recipes plus a Simple Formula to Invent Your Own)
Is that food on my face? Yes, it is! I take great satisfaction in making DIY skincare products out of regular ingredients that I have in the pantry. There are a few reasons:
- If it’s safe enough to eat, then it’s safe enough to put on my skin. I don’t need to worry about reading labels, or trying to decipher chemical names, or battling through greenwash claims.
- Food items are some of the easiest things to find plastic-free and generally packaging-free. Chemicals come in bottles. Coffee grounds, sugar, salt – all of these things can be picked up from bulk stores.
- It keeps my home uncluttered. I like owning things that have multiple uses, and that goes for ingredients as much as for other stuff. One jar with multiple purposes. Plus, it’s kind of fun when you run out of something in the bathroom to just head over to the pantry, rather than traipsing all the way to the chemist.
That said, my bathroom routine is super simple (you can read about it here). Gone are the days when I thought I needed all of those products that the marketers tell us we need. I had the day cream, the night cream, the eye cream, the body lotion, the face scrub, the body scrub… I also had a cluttered bathroom and an empty wallet!
I’m also a big fan of making things that involve little effort. I like to make things from scratch, but I also like these things to take minutes to put together and to be fail-safe (I don’t want to stuff it up and have to throw anything away).
Mixing ingredients together in a jar, now that’s the kind of level of complexity I’m talking about.
DIY Skincare Scrubs from Scratch

Body scrubs exfoliate the skin and remove dead skin cells (there’s plenty of marketing mumbo-jumbo about glowing skin and improved lymphatic drainage and looking 20 years younger, but I’ll spare you any wild claims.) Some body scrubs also moisturise and these generally have an oil base alongside the exfoliating ingredient. I’m a big fan of products with multiple purposes, and I’m also lazy, so any product that can clean, exfoliate and moisturise all in one suits me perfectly!
A good body scrub has three main components: an exfoliator + a moisturiser + essence
By essence I mean more than the fragrance: I also mean the way it makes us feel. For example, lavender is known for its calming and sleep-inducing properties, citrus is energising and awakening, and chocolate feels decadent and indulging.
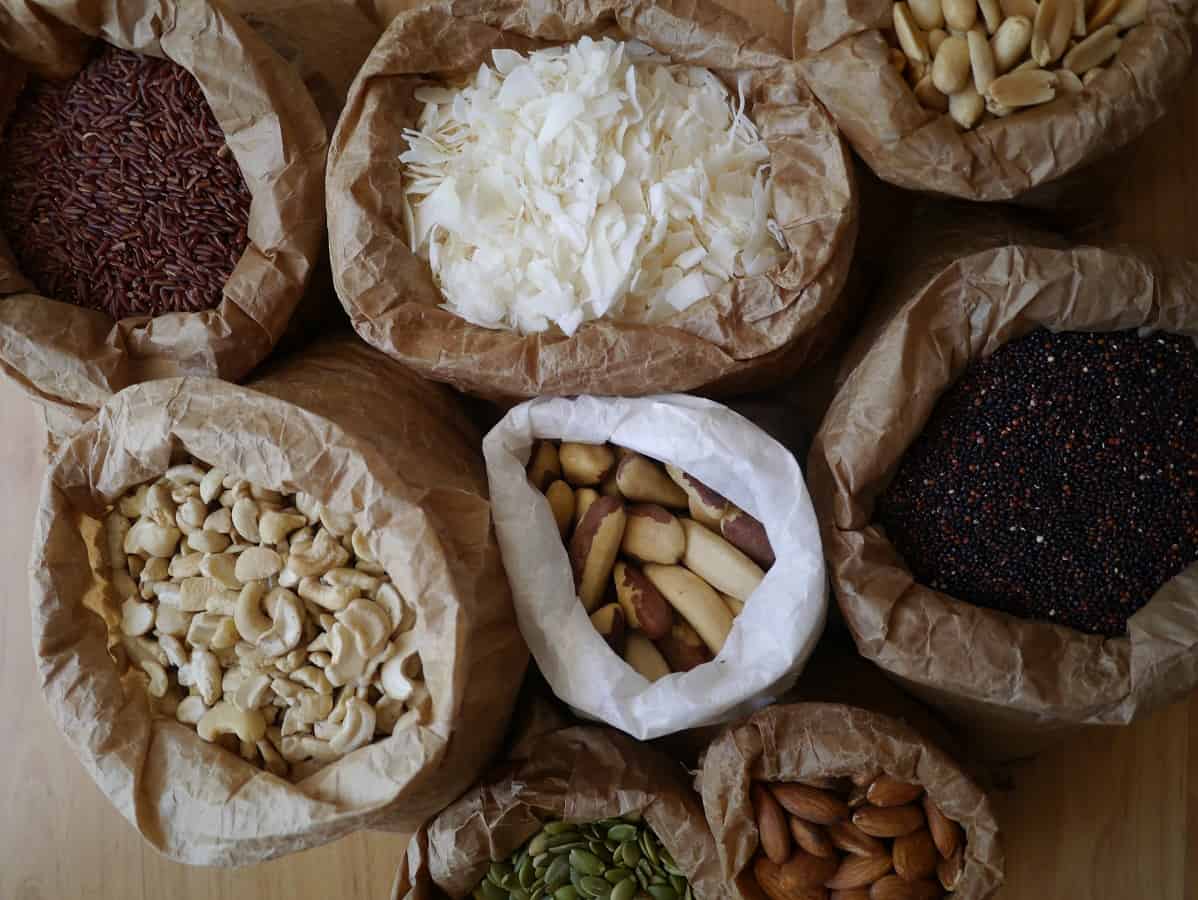
Good Natural Skin Exfoliators
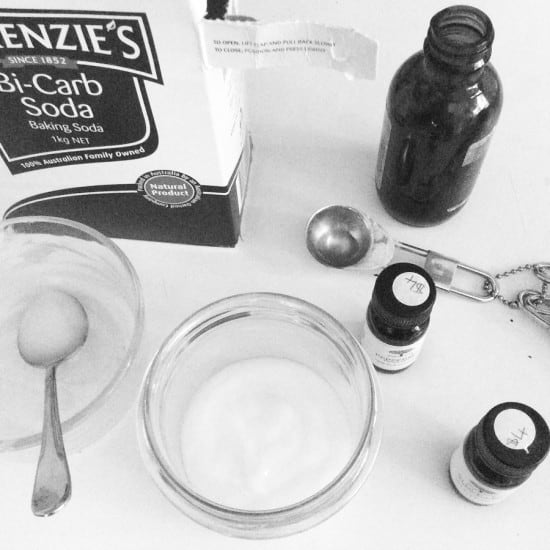
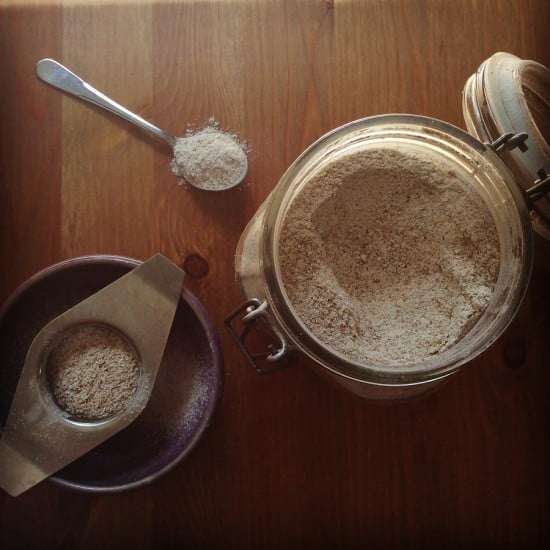
Sugar, salt, dried coffee, used coffee grounds, ground oats, ground rice, bicarb of soda.
Different exfoliators have different properties. Sugar is considered more gentle on the skin than salt as the crystals are smaller and they dissolve more easily in water. Oats and ground rice are gentler on the skin and may be more suitable for face scrubs.
Good Natural Skin Moisturisers
Olive oil, almond oil, jojoba oil, grapeseed oil, sunflower oil, coconut oil.
Oils are not created equal. Some have far superior properties – and often far superior price tags to match. Olive oil is readily available and affordable so is a great optionto start with. It does have a strong fragrance and a green tinge though, whereas almond oil is a more natural colour and without a strong fragrance.
Coconut oil is unusual in that it is solid below 25°C. If you live in a very cold climate you may have a hard time getting a scrub made with coconut oil out of the jar, but if you like the idea of having a more solid product to rub in it’s a good choice.
Ideas For Essences
Essences don’t need to be fancy. You can skip them entirely and leave the scrubs plain if you prefer, or just add a drop of essential oil for fragrance. Or you can go to town, combining essential oils and flower petals and all kinds of things. Up to you.
Stimulating essential oils: grapefruit, lemon, lemongrass, orange, peppermint, bergamont
Relaxing essential oils: lavender, rosemary, cinnamon, ylang ylang, rose, chamomile
Other ingredients to add: lemon, orange or lime zest; lemon, orange or lime juice; lavender flowers or rose petals; honey; thyme or rosemary; cocoa nibs; loose leaf tea (green tea, chamomile tea, peppermint tea).
DIY Body Scrub – a DIY Formula
A body scrub needs to be easy to remove from the jar, spread on your skin and rinse off.
Start with a tablespoon of your chosen oil, and a tablespoon of your chosen exfoliator, and combine. Add more of either to get your preferred consistency. Add your essences last.
If adding dried herbs, flowers or tea you may need a little more oil, as these will soak up the oil.
If adding lemon, lime or orange juice, you may prefer a little less oil as these will add more liquid to the pot.
Test it out! Always do a patch test first. Put a small amount on your skin in the crease of your elbow, and wait 24 hours to see if there is any adverse reaction. Use it in the shower, and see if you like the consistency. Make a note of any adjustments you might want to make. Test on your body before trying on your face as your facial skin is more fragile, and always avoid the eye area.
DIY Body Scrubs: 4 Recipes to Get You Started

From left to right: citrus olive oil scrub; coffee scrub; lavender sugar scrub; green tea and epsom salts scrub.
These are some ideas to get you started – feel free to play with the ingredients you have to hand and make your own combinations. All of these scrubs are fresh and do not contain preservatives, so are best stored in the fridge and/or used within a couple of weeks.
Citrus Olive Oil Scrub

Ingredients:
2 tbsp olive oil (30 ml)
1/2 cup sugar
2 tsp lime zest
juice of 1/4 lime
Optional: a drop of lemon, grapefruit or lime essential oil
Mix together the sugar and oil. Add the lime zest and lime juice, and essential oil if using. You can add extra sugar or oil to get your desired consistency. Spoon into a glass jar.
Allow the scrub to settle. A layer of olive oil on the top of the jar will help keep it from spoiling. Stir before use.
Coffee Scrub

Ingredients:
2 tbsp spent coffee grounds (ask a local cafe for their used grounds)
2 tbsp sugar
2 tbsp coconut oil
Optional: a drop of orange essential oil
Method: melt the coconut oil if solid, and mix the coffee, sugar and oil together. Add the essential oil last. Store in a glass jar in the fridge.
I love using coffee grounds as they are a waste product. You could use fresh coffee, but why wouldn’t you want to have a cup of coffee first?! If you use homemade coffee grounds, let them dry out as the extra moisture will mean it spoils more quickly. There’s no reason why you couldn’t use olive oil instead of coconut oil. I just like to experiment :)
Lavender Scrub

Ingredients:
3 tbsp almond oil
1/2 cup sugar
2 drops lavender essential oil
Optional: 2 tsp dried lavender flowers
Method: mix the oil and sugar together, then add the flowers and essential oil.
You could substitute the lavender flowers for chamomile flowers or rose petals, and lavender essential oil for chamomile or rose geranium. Almond oil works better than olive oil as the delicate floral flowers can be overpowered by the olive.
Green Tea Scrub

Ingredients:
3 tsp Epsom salts
3 tsp bicarb
1 tsp matcha powder
3 tbsp olive oil
Mix the dry ingredients together, then add the olive oil. Pour into a glass jar.
Epsom salts are not actually salt, but a mineral compound containing magnesium which is thought to be very good for the skin. If you can’t find Epsom salts, regular salt or sugar will be fine. If you don’t have matcha powder, you can use regular green tea.
Now I’d love to hear from you! Do you make your own skincare products? Do you want to, or is it something you can’t see yourself bothering with? Do you have your own favourite recipes or flavour/scent combinations? Are there any other products you make from scratch? Have you ever had any disasters, or things not going to plan? Any tips you’d like to add? I’d love to hear from you, so whether you’re a DIY skincare enthusiast or avoid it at all costs, please leave me a comment telling me your thoughts!
<
p style=”text-align: center;”>[leadpages_leadbox leadbox_id=1429a0746639c5] [/leadpages_leadbox]
Disclaimer: the information here is provided for information purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. It is a record of my own experiences. Always do your research before using ingredients on your skin, particularly when using essential oils.