From landfill to refill: cleaning products that clean the ocean
This post is a sponsored collaboration with Zero Co.
When I started my waste journey back in 2012, I primarily wanted to reduce my plastic. A few month in I realised that reducing waste isn’t just about the plastic, and so I worked on reducing all my single-use packaging – metals, paper, cardboard, steel and aluminium as well as plastic – and of course, reducing my food waste.
I even went as far as the ‘fitting a year’s waste in a jam jar’ challenge.
And what I realised from that challenge is this: whether or not I can fit my waste into a jam jar or not is not the point. (And frankly, who cares?) If a handful of people can fit their waste into a jam jar, it’s not really game-changing stuff.
It’s definitely not where I want to be focusing my attention.
I’m much more interested in how we can get everybody reducing their waste, whether it’s 90 per cent or 50 per cent or even 10 per cent.
Much better to have everybody doing something rather than a few people doing everything.
And for everybody to be doing something, we need options. There’s no one way to reduce waste. What works for some of us will never work for all of us. The more alternatives, the better.
Zero Co and their mission to untrash the planet
I’m going to confess, the first time I came across Zero Co, it was hard to see past the plastic. Even though my views have changed on plastic since my first plastic-free month challenge back in 2012, I’d still rather see as little plastic as possible.
Zero Co make (palm oil free, greywater safe, plant-based, vegan) cleaning and personal care products. And although it’s plastic, the the packaging that they use to distribute their products is not single-use – the containers are made out of recycled ocean plastic and the pouches are returnable and refillable, to be used and reused over and over.


When I heard about their model, I was intrigued.
As much as I dislike plastic, I dislike single-use even more. Anything that can be used again and again and again is a better use of resources than single-use. For me, it’s about the waste, and how we reduce it.
So yes, I was intrigued, but I had a lot of questions.
(Like, how much ocean plastic? From which ocean? Who collects it? How are the pouches refilled? How many times?)
And so I emailed them, and we had a great back and forth, and then I poured over their website and sent a bunch more questions.
And I’m happy to say that I learned a lot, and I changed my mind.
Zero Co offered to send me a box of their products to try so I could test their products, the packaging and the return system. (And we had an agreement that if I didn’t like the products, there was no expectation to share with you. And if I did share, that I’d be honest and tell it like it is.)
But I think their re-use model is interesting and their transparency is refreshing. That’s how they won me over. It’s one thing to pledge to do things, but quite another to showcase how.

How it works: the Zero Co circular economy (reuse) model
Zero Co have a mission to “untrash the planet” through stopping the production of new single-use plastic, and by cleaning up the plastic already in the oceans.
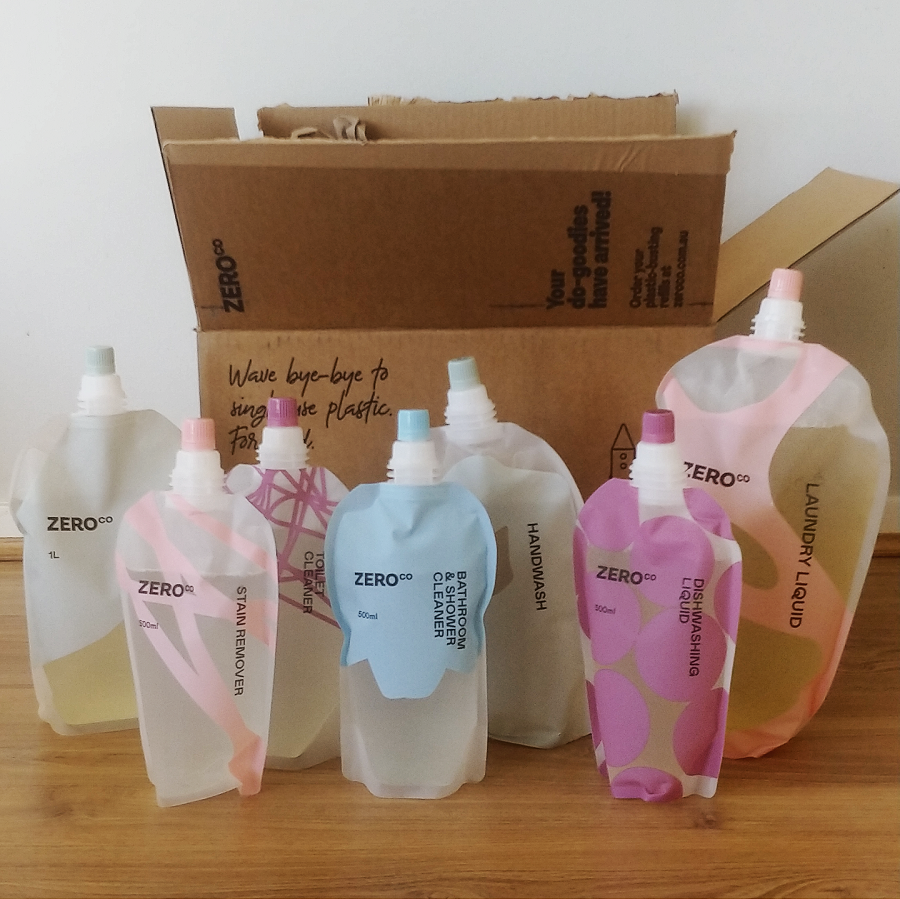
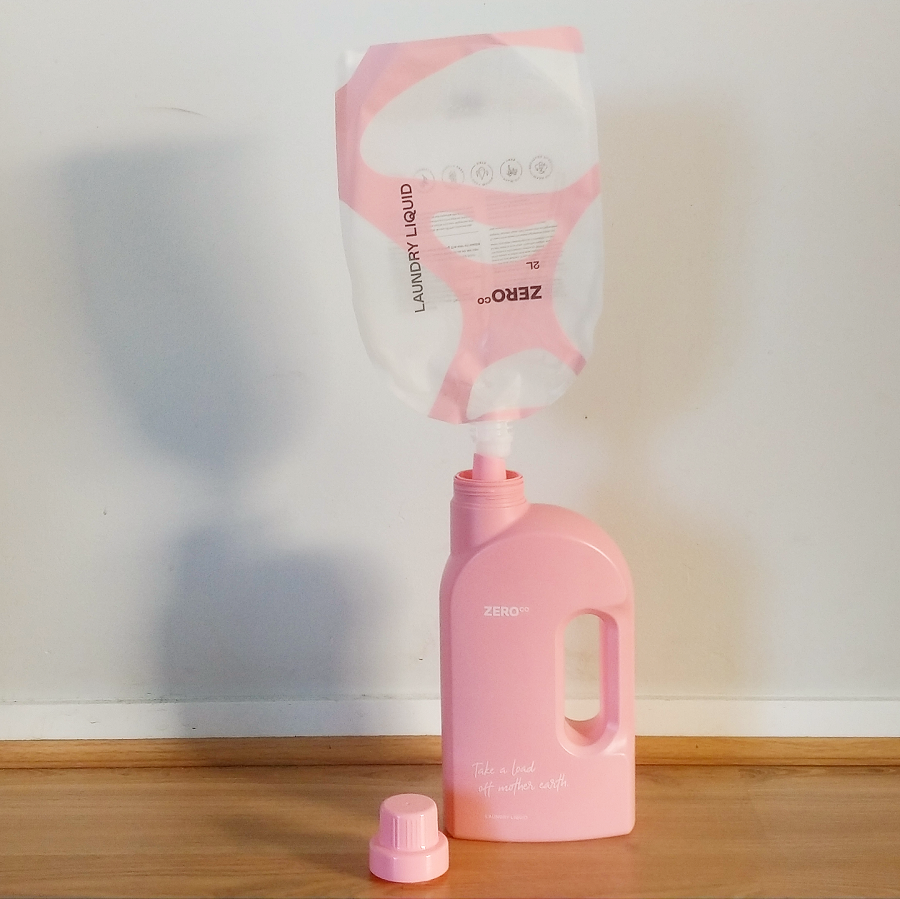
They do this by distributing cleaning products in reusable, refillable pouches. The dispensers (which you can choose to use with your refills) are made of ocean plastic.
You order the products you want (all packaged in the pouches) and if you need them, you also order the dispensers. They are shipped to your home with no additional plastic packaging.



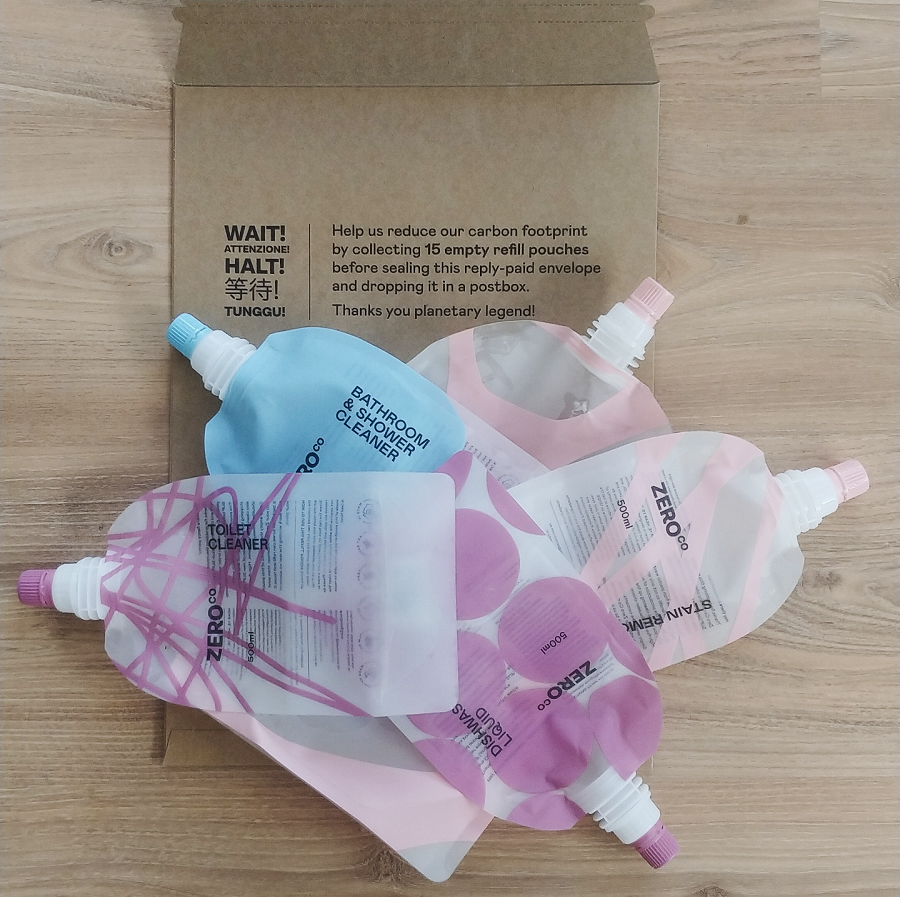
The box contains a reply-paid (cardboard) envelope for the empty refill pouches. Once you have 15 empty pouches, you send it back for the pouches to be reused.
They describe the model as “like the milkman, reimagined.”

Sounds good so far, but I’m a details person. Luckily, they provided the details.
Ocean plastic
The ocean plastic used in the dispensers is collected from the waters outside Jakarta, Indonesia, via an initiative called Ocean Waste Plastics. Local fishermen collect the plastic, which they sell to Pack Tech, who reprocess the plastic into (amongst other things) the Zero Co dispensers.
These dispensers contain 70% recycled ocean plastic, and 30% non-ocean recycled plastic.
So far, Zero Co have pulled 6,000kg of plastic from the ocean to make their dispensers.
OCEANS 21
One of Zero Co’s newest initiatives is OCEANS21, which has the goal of collecting 21 tons of Australian ocean-bound plastic waste, to turn into Zero Co bottles.
From March until May 2021, Zero Co will invest $5 from every starter box sold to fund their ocean clean-up projects. Their launch event will be in Sydney where they will be making a record-breaking attempt to clean up Sydney Harbour.
From there they will head to Cape York – but they are also working on some more local and grassroots initiatives.
Refillable pouches
The refillable pouches are made of 40% recycled plastic, and are designed to be refilled 100 times. (Yes, it would be great to use 100% recycled plastic, but they found that this compromised how many times the pouches could be refilled – 40% seemed to be the sweet spot.)

Carbon emissions
There’s always going to be a higher footprint with delivery models versus getting refills at a bricks-and-mortar store. It’s worth remembering that not everyone has access to a bulk store that sells cleaning products. To combat this, Zero Co use couriers that carbon-offset their emissions, and ask that empty pouches are not returned until there are 15 of them, to reduce transport emissions and packaging.
They are also looking at how they might get their products into brick-and-mortar stores in the future, whilst maintaining the circular reuse model.
Zero Co Products – a review
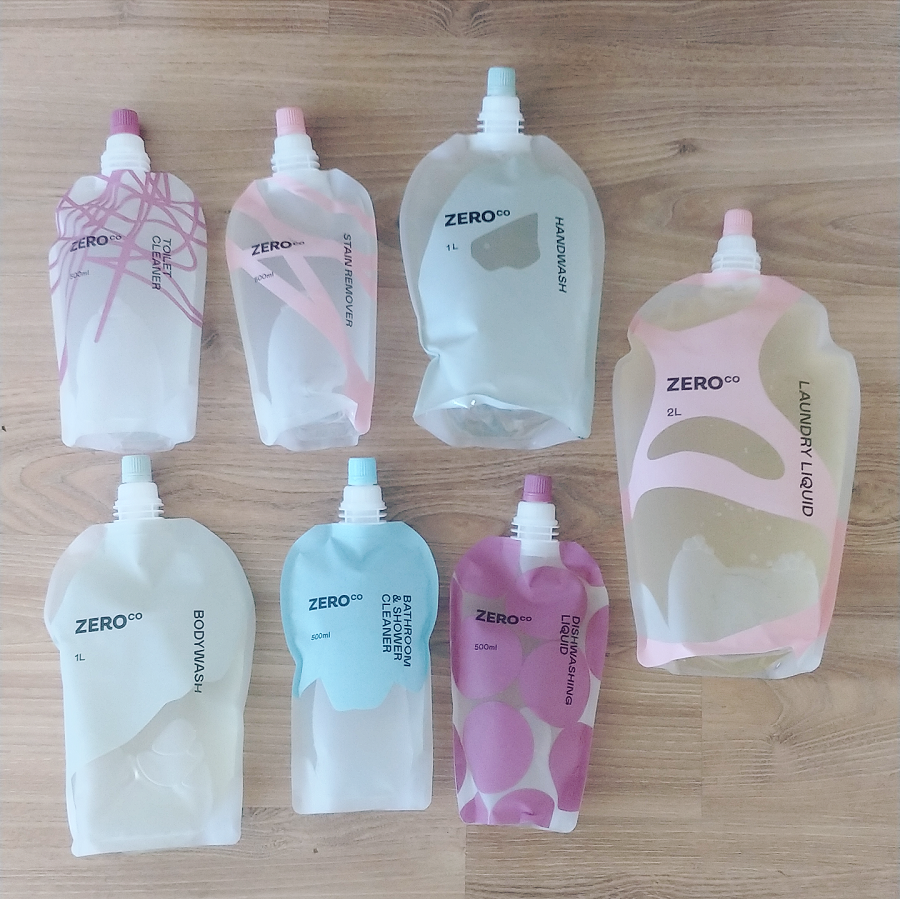
The core range of Zero Co products includes air freshener, bathroom and shower cleaner, bodywash, dishwasher tablets, dishwashing liquid, handwash, laundry liquid, stain remover and toilet cleaner.
(They have just finished reformulating the multi-purpose cleaner, which is part of their core range but whose shipping was delayed.)

They also have plans to launch shampoo, conditioner, toothpaste and deodorant later in the year, but no firm dates on these yet.
I didn’t try the air freshener, as this is a product I’d never use, and I didn’t try the dishwasher tabs because I don’t have a dishwasher.
And yep, all the products I received worked as they are meant to do – they clean!
(To me, cleaning products are cleaning products are cleaning products – except when they don’t work at all. These worked just as well as any cleaning product I’ve ever bought at the bulk store. But don’t just take my word for it, because since when was cleaning one of my strengths? Zero Co went to the trouble of getting their products tested by an independent lab.)
The one notable feature of all these products is that they are very strongly fragranced. I tend to use unfragranced or lightly fragranced products, and this was quite a shock to my senses. Most of their fragrances are based on essential oils, so it’s not artificial fragrance, it’s just… strong.
(You can read their ingredient lists here.)
This is probably a polarising feature, so it’s worth pointing out.
Someone on my local zero waste Facebook group recently was asking about zero waste laundry detergent with a long-lasting fragrance as she said she was sick of her laundry smelling of “wet clothes”, and a lot of people recommended Zero Co. I actually really like the Zero Co laundry liquid for washing my for towels and linen, particularly when it’s going in the cupboard.

I also found that the strong fragrance of the bodywash and handwash means I use a lot less, which makes the products go further.
But if strong-scented cleaning and personal care products are not your thing, this will be a dealbreaker.
(I wonder in the future if they will launch an unscented range, but for now there isn’t one.)
Could Zero Co products be for you?
As I said at the start, there’s no one zero waste product or idea that works for everybody.
Zero Co probably won’t work for you if:
- You already buy all your personal and cleaning products at the bulk store, and you’re happy with them;
- You DIY all of your own personal and cleaning products;
- You dislike strong fragrances;
- You live outside Australia (so far they only ship within Australia, but they are looking at overseas options).
Zero Co might be something to consider if:
- You currently buy products in single-use packaging;
- You don’t have access to a bulk store (for example, living in regional areas);
- You don’t have time to get to the bulk store regularly, or you’re not happy with the products on offer at the bulk store;
- You like the idea of a one-stop shop for all your products;
- You want to support an Australian start-up on a mission;
- You like strongly fragranced products.
(If you have any questions, their FAQ page is probably one of the most thorough I’ve ever come across. So be sure to have a read.)
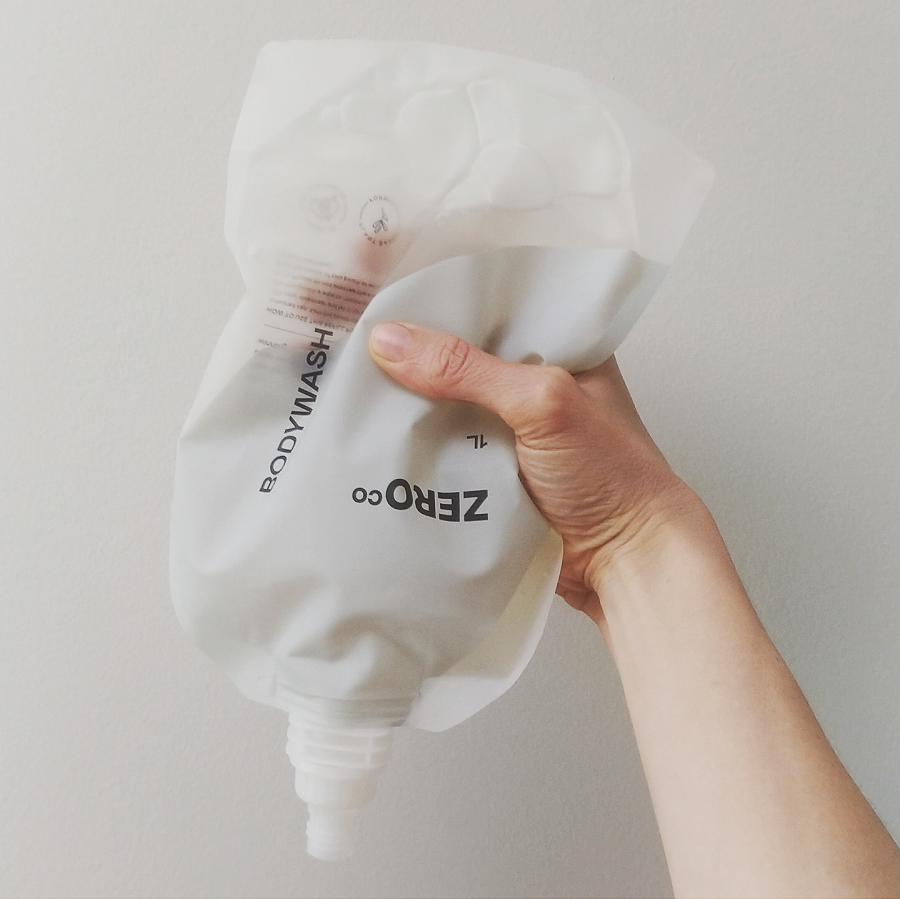
If you’d like to try their products, Zero Co have very kindly offered a discount to my readers. Use the code TREADING10 which will give you $10 off all products (new customers only, one use per customer, minimum purchase $80. Don’t forget you can always go halves with friends or family if you don’t need quite this much, and don’t want to stockpile!).
Visit the Zero Co website here.
[leadpages_leadbox leadbox_id=1429a0746639c5] [/leadpages_leadbox]