Why Tetra Paks aren’t green (even though they’re ‘recyclable’)
Tetra Paks are the cartons you find in the shops that are used to package long-life milk, juice and various other liquids. You can also find products like chopped tomatoes packaged in this way. These containers allow food to be protected from contamination by bacteria and other microbes, meaning products can sit on the shelf for months without going bad.
Once they’re used, Tetra Pak assure us that they can be recycled.
That sounds great, but I was left wondering…how exactly are Tetra Paks recycled? Aren’t they made up of layers of different material? Is it even possible to separate them, and then what happens to the materials?
After some investigating, my conclusion is that Tetra Paks aren’t a green solution at all. Here’s why.

What is a Tetra Pak made from?
Tetra Paks are made up of a number of components which are layered: paperboard (made from wood), polyethylene (a type of plastic) and aluminum. These different components give Tetra Paks their unique properties: keeping the liquids in but the microbes out, and a strong but lightweight container.
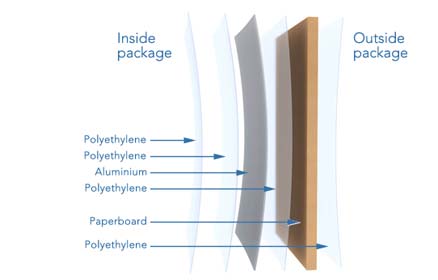
When a Tetra Pak is recycled, all these component parts need to be separated out.
What Does Recycling Mean?
Whilst recycling can be thought of as a way of converting waste into a new material, more accurately it means a process to return material to a previous stage in a process that operates as a cycle. After all, the word is “re-cycling”. The idea is to take a used product and turn them back into the same type of product, such as glass bottles being melted down and formed into new glass bottles. There is no loss of quality, so this recycling of glass can go on forever.
When a product doesn’t get turned back into the same product, but one of lesser quality (as with plastic recycling) it isn’t recycled, it’s downcycled. Products that are downcycled often only undergo a limited number of cycles (maybe as few as 2) before reaching the end of their useful lives and ending up in landfill.
For Tetra Pak to be truly recycled, these layers of paperboard, polyethylene and aluminium would need to be separated out, and reformed to make new Tetra Pak cartons. However, that isn’t what happens.
How is a Tetra Pak Recycled?
I’ve found not one, but two different videos that explain how Tetra Paks are recycled: how they are sorted into their component parts and what happens to these parts.
The first is a somewhat cheesy video from India, which seems to be a Tetra Pak promotional video that lasts four minutes. The second is a UK/German video that runs for less than two minutes.
Whilst you watch them, think about the following:
- How much energy is involved in the process?
- How are the post-recycled materials used?
- Where is the ‘cycle’ part of the process?
Why Tetra Paks aren’t Sustainable
If Tetra Paks are recyclable, why aren’t they green? Let’s look at the different components, where they come from and what happens to them once the cartons are empty.
Paperboard (Wood)
Tetra Pak have devoted a significant amount of their website space to telling customers how sustainable their containers are. As well as talking at length about Tetra Paks being recyclable, they inform us that Tetra Pak source FSC-certified wood for 41% of their cartons worldwide (2013 figure). This equated to 32 billion FSC-labelled Tetra Paks reaching consumers in 2013.
Let’s look at this another way.
If 32 billion containers is 41%, then the amount of non-FSC wood Tetra Paks reaching consumers would be 46 million. 46 million containers made from non-renewable sources? That is a lot of wood. Tetra Pak might have a goal to reach 100% FSC-wood, but it isn’t happening now.
When this paperboard is recycled, it isn’t turned back into new Tetra Paks. It is unclear whether this is because their paperboard needs to come from virgin sources to avoid contamination (as is the case with plastic), or whether the quality of the recycled paperboard isn’t high enough to make new cartons, or some other reason. Whatever the reason, it is turned into office paper.
Plastic and Aluminium
The other two layers of the Tetra Pak, polyethylene (plastic) and aluminium, cannot be separated by the recycling process and remain combined as a “polymer”. The uses for this “polymer” is in the cement industry, or as low-cost housing material. The question arises, is there a genuine demand for this product, or is there a market because of an abundant supply of this waste material?
The fact that it gets reused and isn’t sent to landfill is great, except it doesn’t serve to make Tetra Paks a “green” solution. These cartons use fresh plastic and aluminium to make their cartons, and the waste products becomes something else entirely. Thus it is a linear system, not a cycle – and anything that is linear cannot be sustainable long-term.
A Word on Recycling Tetra Paks
The other thing to alwyas remember about recycling, is just because something can be recycled, it doesn’t mean that it will be recycled. The two are very different. For example, in the UK access to recycling facilities is as high as 85%; in the USA it’s nearer 40%, and in other countries like China, considerably less. Tetra Pak estimate global recycling was less than 25% in 2013. In Denmark in 2007, 33% of Tetra Paks were incinerated: resources turned to toxic ash.
The Conclusion
Tetra Pak may want to be sustainable; they may want to use 100% FSC wood and achieve 100% recycling rates, but they still have a long way to go. Even if they achieve this, there’s no getting away from the fact that Tetra Pak production is a linear process. Tetra Paks are turned into different post-consumer products, meaning a constant supply of fresh virgin material (wood, oil and aluminum) is needed for their manufacture.
Tetra Paks – What Are The Alternatives?
- Choose glass over Tetra Pak containers. Glass can be truly recycled back into new glass products. You can find wine, milk, juice and oil in glass so there’s no need to buy Tetra Paks for these items.
- For items like chopped tomatoes, use steel cans, which can also be truly recycled.
- Consider refillables, or making your own. Juicing your own fruit is far tastier than drinking pasteurized syrupy juice in cartons, and healthier too!
- If you can’t avoid Tetra Paks, skip the single serve containers. Buy the largest size and decant into individual containers for lunches or when you’re out and about.
Did you know that Tetra Paks contained plastic and aluminium, and that they cannot be truly recycled? Did any of the statistics surprise you? Are Tetra Paks something that you regularly buy? I’d love to hear your thoughts on this so please leave a comment below!
[leadpages_leadbox leadbox_id=1429a0746639c5] [/leadpages_leadbox]



